Vortex flow meters are widely used for measuring steam due to their durability, high temperature tolerance, and minimal maintenance. However, wet steam can cause significant issues for vortex meters, leading to inaccurate readings or complete failure. In this article, we will explore why vortex meters struggle with wet steam and how to prevent or fix these problems to maintain accurate steam measurement.
🧪 What Is Wet Steam?
Wet steam refers to steam that contains liquid water droplets, typically due to partial condensation. It often occurs during:
Start-up or shutdown phases in steam systems
High-pressure drops in the steam pipeline
Inadequate insulation or heat loss
Key Characteristics:
Mixture of gas and liquid: Steam is not fully vaporized.
Condensation: Water droplets are present within the flow, altering the density and behavior of the steam.
⚠️ Why Vortex Flow Meters Fail in Wet Steam
Vortex flow meters rely on stable vortex shedding from a bluff body in the flow. This shedding frequency is proportional to the velocity of the flow, which is typically a clean gas like dry steam.
However, wet steam can cause several issues that lead to failure or reduced accuracy:
1. Erratic Vortex Shedding
When wet steam passes through the vortex meter, the water droplets disturb the flow. These droplets interfere with the vortex shedding process, causing irregular vortex patterns. This results in fluctuating or inaccurate flow readings.
Effect: Signal instability, causing loss of accurate flow measurements.
2. Damage to Sensor Elements
The presence of liquid water droplets can physically damage or corrode the vortex meter’s sensors and electronics over time, especially if the flow is turbulent.
Effect: Accelerated wear, leading to expensive repairs or replacement.
3. Incorrect Mass Flow Calculation
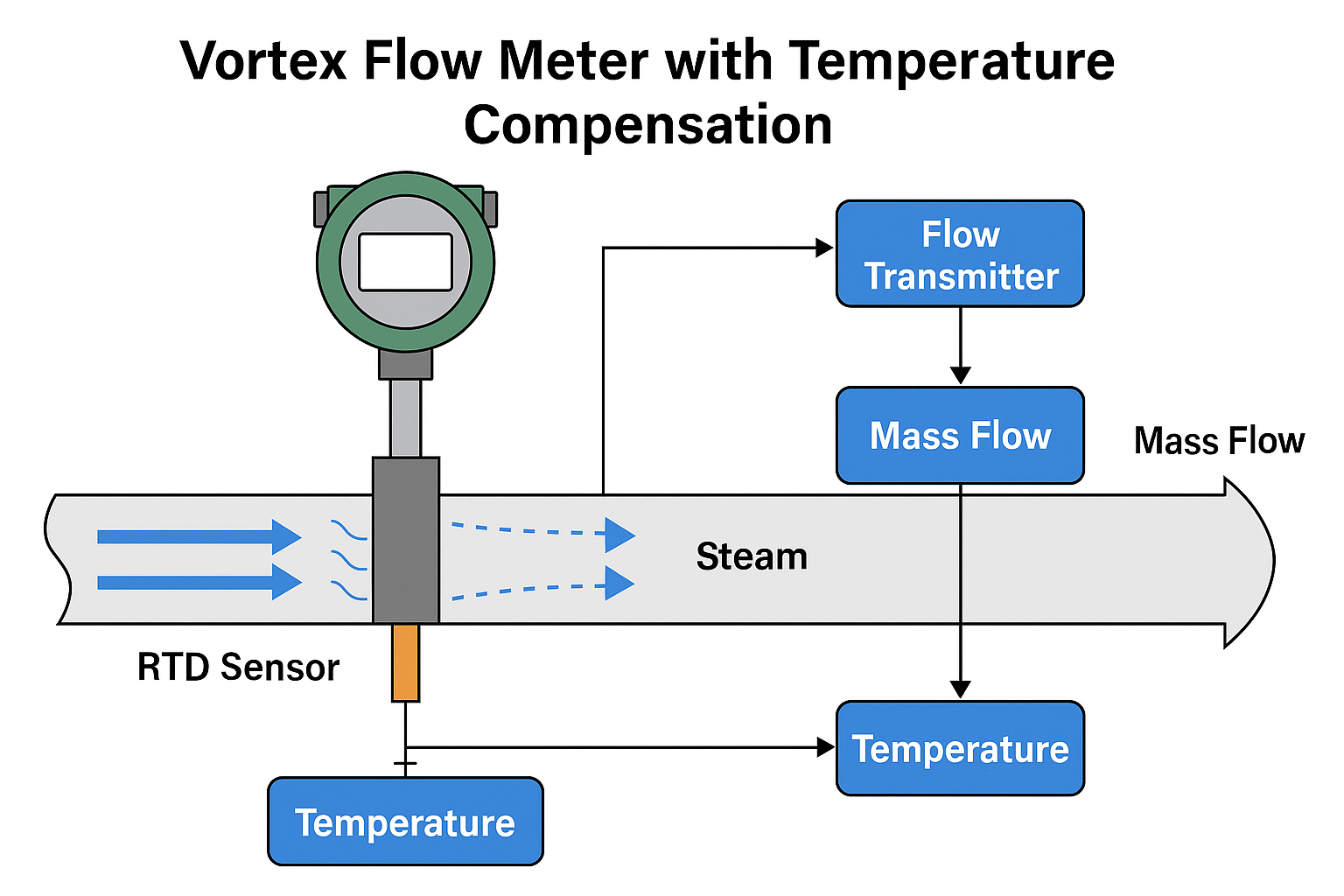
Vortex meters measure volumetric flow, but to get mass flow, temperature and pressure compensation is required. Wet steam can result in inaccurate mass flow calculations because the density of the steam is altered by the water content.
Effect: Incorrect energy calculations, billing, or process control.
4. Clogging and Fouling
In certain applications, wet steam may contain contaminants or impurities that can accumulate on the meter’s bluff body. This can lead to clogging and a significant drop in measurement accuracy.
Effect: Maintenance issues and need for more frequent cleaning.

🔧 How to Fix Vortex Flow Meter Issues in Wet Steam
While wet steam presents several challenges, there are ways to mitigate or even eliminate the problems to ensure accurate measurements.
1. Use a Separator or Strainer
Installing a steam separator or filter upstream of the vortex flow meter helps remove excess water from the steam before it enters the meter. This will ensure only dry steam enters the vortex meter, improving measurement accuracy and reducing damage risks.
How it helps: Reduces water content, improving vortex stability.
2. Install a Steam Trap
A steam trap collects and removes water from the steam pipeline. This ensures that the steam entering the vortex meter is as dry as possible, significantly reducing the risk of inaccurate readings caused by wet steam.
How it helps: Prevents condensate build-up in the pipeline.
3. Temperature and Pressure Compensation
If the system cannot eliminate all wet steam, using temperature and pressure compensation with your vortex meter can help improve accuracy. The flow meter can adjust its calculations for density variations caused by moisture in the steam.
How it helps: Improves mass flow accuracy by accounting for density changes.
4. Use Inline Strainers or Cleaners
Regular cleaning of the vortex meter’s bluff body and sensor can help reduce the impact of fouling due to moisture. An inline strainer can remove debris, and scheduled maintenance can keep the meter working properly.
How it helps: Keeps the sensor free from debris, maintaining reliable readings.
5. Select a Suitable Vortex Meter Model
Not all vortex meters are the same. Some models are specifically designed to handle wet steam and have improved internal design features to withstand moisture and high-temperature steam.
How it helps: Durability and performance are enhanced in wet steam applications.

📌 Conclusion
Vortex flow meters can experience significant problems when used with wet steam, primarily due to the interference of water droplets with the vortex shedding process. However, by using proper pre-conditioning techniques such as installing separators, steam traps, and compensating for temperature and pressure, you can minimize the impact of wet steam on vortex meters.
Key takeaways:
Wet steam can cause signal instability, sensor damage, and incorrect mass flow calculation.
Solutions include steam separation, temperature/pressure compensation, and regular maintenance.
Select appropriate vortex meter models designed to handle steam conditions.
By implementing these best practices, you can ensure that your vortex flow meter operates accurately and reliably, even in challenging steam conditions.
